What is the cheapest energy? The energy that is not used!
Heat recovery ventilator (hrv): a must for airtight homeS
 Each day, we ingest 1 kg (2.2 pounds) of food, drink 3 kg (6.6 pounds) of liquids and breathe 30 kg (66 pounds) of air! We must, therefore, have a permanent supply of fresh air in our homes. However, the Quebec climate is such that 50% of our energy consumption is used for heating. Considering the costs involved, we must not allow cold air to enter our homes directly from the outside, nor should we incur heat loss by allowing warm air from our homes to escape outside. The heat recovery ventilator (HRV), mandatory in new homes, is thus a solution for dealing with this problem.
Each day, we ingest 1 kg (2.2 pounds) of food, drink 3 kg (6.6 pounds) of liquids and breathe 30 kg (66 pounds) of air! We must, therefore, have a permanent supply of fresh air in our homes. However, the Quebec climate is such that 50% of our energy consumption is used for heating. Considering the costs involved, we must not allow cold air to enter our homes directly from the outside, nor should we incur heat loss by allowing warm air from our homes to escape outside. The heat recovery ventilator (HRV), mandatory in new homes, is thus a solution for dealing with this problem.
Whether it is a stand-alone device or centralized, the HRV provides aeration and pre-heating or cooling of the air in the home by extracting heat from the exhaust air. By preheating or cooling down the air coming from outside, whichever the case, the HRV is an essential device to limit expenditures for heating or air conditioning.
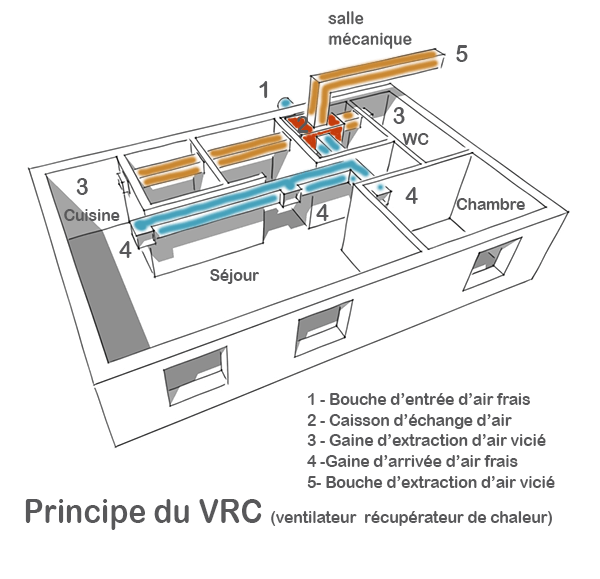
HOW DOES IT WORK?
In a heat recovery ventilator (HRV) two fans are in the same box where they force air through a heat-exchanger core. The HRV allows for the heating of new air by exhausting stale air, or by cooling it down, depending on whether the system is in heating or air conditioning mode.
The first fan brings fresh air into the house and the other exhausts indoor air. Only heat is exchanged; the air coming from the inside will never contaminate the new air.
To be assured of its energy efficiency, an approved ENERGY STAR® and HVI (Home Ventilating Institute) model should be chosen. Of equal consideration, the HRV must be installed in a heated place and be easily accessible in order to facilitate its inspection and cleaning. The cold air ducts must be insulated in order to prevent the formation of condensation and mold growth.
- A few facts and figures :
- The HRV can fully renew the air in a home in just 3 hours without compromising the home’s thermal comfort
- The colder it is outside, the more energy efficient the HRV becomes; at an outside temperature of -250C (-130F), between 60% and 80% of the heat can be recovered
- For a small home, the HRV allows for an annual savings of more than $100

